초록접수 현황
| 17F-145 | 구연 미채택시 포럼 발표 |
The Role of Partial Arch Repair in Acute Type I Aortic Dissection Presented with Stroke
Won Gi Woo¹, Suk-Won Song¹, Woon Heo¹, Tae Hoon Kim¹, Yoo-Jeong Lee¹, Kyung-Jong Yoo², Bum-Koo Cho³
¹Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea., ²Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea., ³The Korea Heart Foundation, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Purpose : In acute type I aortic dissection (AIAD) with stroke, the surgical outcome is known to be worse than non-stroke patient. We sought to find its incidence and characterize the factors associated with prognosis.
Methods : From 2010 to 2017, 240 patients underwent AIAD repair (mean age 58.1±14.1, 137 [57.1%] male). Stroke was present at arrival in 42(17.5%) patients. Radiological findings of arch vessels were reviewed. And status of activity of daily living (ADL) were classified in three groups (dependent, assisted and independent) at discharge and dependent ADL was defined as patients who need full assist for ADL.
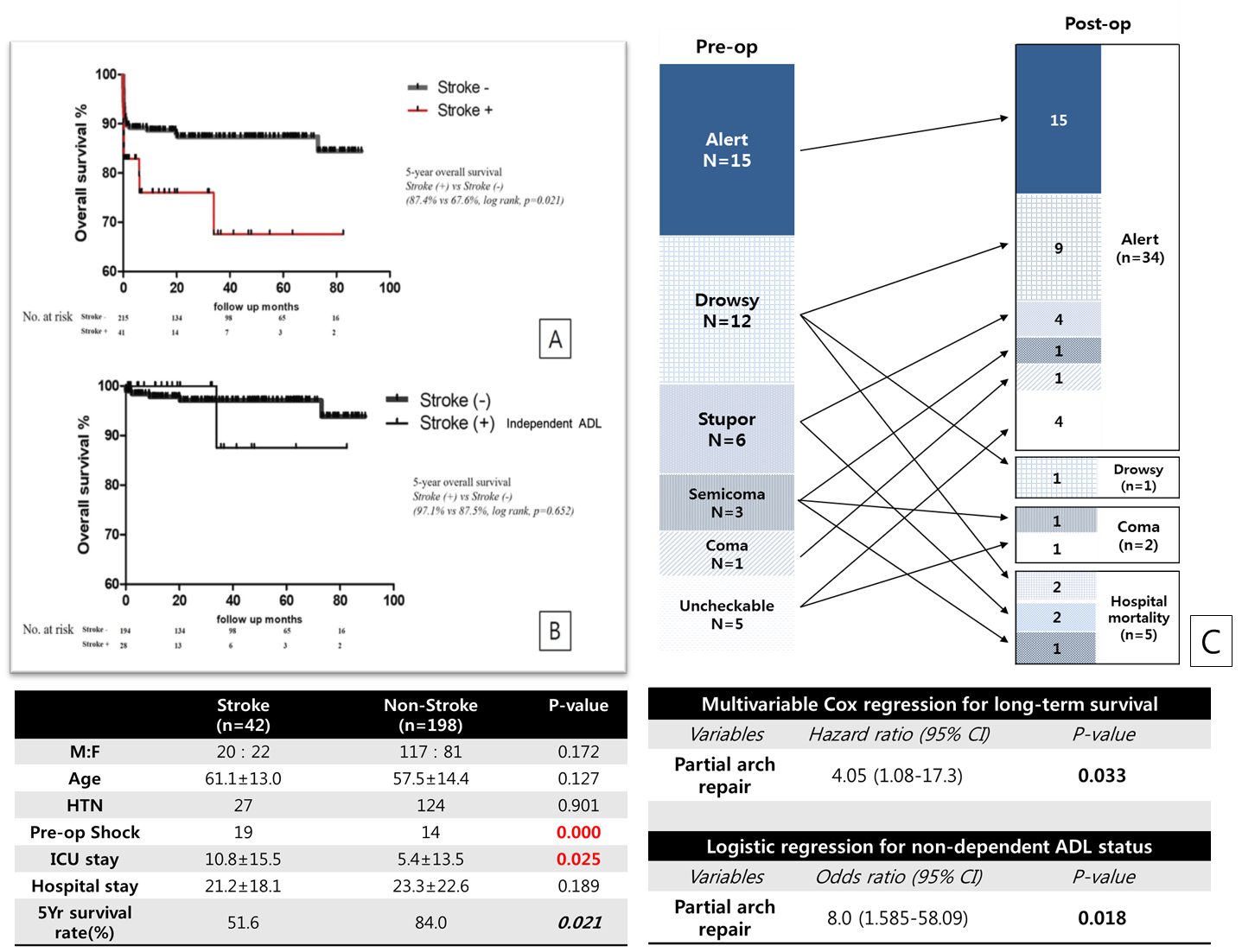
Results : Twenty three(54.8%) presented with hemiplegia, and 27(64.3%) were not alert. The mean interval from symptom to repair was 12±22hrs and in-hospital mortality occurred in 5(11.9%)patients, 10(23.8%) were dependent ADL and most of patients experienced improvement in mental status after repair(fig C). In pre-op CT angiography, 19(45.2%) patients had innominate artery(IA) involvement of dissection with various degree of true lumen patency. Compared to non-stroke AIAD patient, stroke group had worse 5-yr survival rate(fig A, 84.0% vs. 51.6%, p=0.021). However, non-dependent ADL patients in stroke presented similar long term survival rate with non-stroke(fig B, 97.1% vs. 87.5%, p=0.262). Furthermore, Multivariable Cox and logistic regression show that the partial arch repair(at least including IA replacement) was the only independent factor for long-term survival (p=0.033, HR 4.05) and non-dependent ADL(p=0.018,OR 8.0).
Conclusion : In AIAD patients with stroke, dissection flap is frequently involved in innominate artery. Therefore the partial arch repair seems to be appropriate and promise favorable long-term survival, and independent ADL of patients.
Methods : From 2010 to 2017, 240 patients underwent AIAD repair (mean age 58.1±14.1, 137 [57.1%] male). Stroke was present at arrival in 42(17.5%) patients. Radiological findings of arch vessels were reviewed. And status of activity of daily living (ADL) were classified in three groups (dependent, assisted and independent) at discharge and dependent ADL was defined as patients who need full assist for ADL.
Results : Twenty three(54.8%) presented with hemiplegia, and 27(64.3%) were not alert. The mean interval from symptom to repair was 12±22hrs and in-hospital mortality occurred in 5(11.9%)patients, 10(23.8%) were dependent ADL and most of patients experienced improvement in mental status after repair(fig C). In pre-op CT angiography, 19(45.2%) patients had innominate artery(IA) involvement of dissection with various degree of true lumen patency. Compared to non-stroke AIAD patient, stroke group had worse 5-yr survival rate(fig A, 84.0% vs. 51.6%, p=0.021). However, non-dependent ADL patients in stroke presented similar long term survival rate with non-stroke(fig B, 97.1% vs. 87.5%, p=0.262). Furthermore, Multivariable Cox and logistic regression show that the partial arch repair(at least including IA replacement) was the only independent factor for long-term survival (p=0.033, HR 4.05) and non-dependent ADL(p=0.018,OR 8.0).
Conclusion : In AIAD patients with stroke, dissection flap is frequently involved in innominate artery. Therefore the partial arch repair seems to be appropriate and promise favorable long-term survival, and independent ADL of patients.
책임저자: Suk-Won Song
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
발표자: Won-Gi Woo, E-mail : 1keywoo@yuhs.ac








