초록접수 현황
| 17F-186 | 구연 발표 |
The Influence of Hepatic Dysfunction on Patients undergoing Tricuspid Valve Surgery.
Hyung Gon Je¹, Mi Hee Lim¹, Sang-Kwon Lee¹, Ji Hye Lee², Hye Lim Oh²
¹Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea., ²Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea
Purpose : Hepatic dysfunction(HD) is frequently combined with chronic tricuspid regurgitation(TR) and considered a risk factor for surgery. Late referral is associated with not only progression of disease but also surgical morbidity and mortality. We compared the clinical outcomes of TR surgery in patients with or without HD, and evaluated changes in liver function following TR surgery.
Methods : Among 159 consecutive patients who underwent tricuspid valve surgery from October 2008 to July 2017,101 patients with moderate or severe TR were included. We divided the patients into with the normal liver function(N;n=47) and HD(n=54) groups. The definition of HD was clinically or radiologically diagnosed liver cirrhosis(n=15) or preoperative model for end-stage liver disease(MELD) score ≥13 (n=50). Perioperative variables were compared and changes in simplified MELD score following surgery were determined.
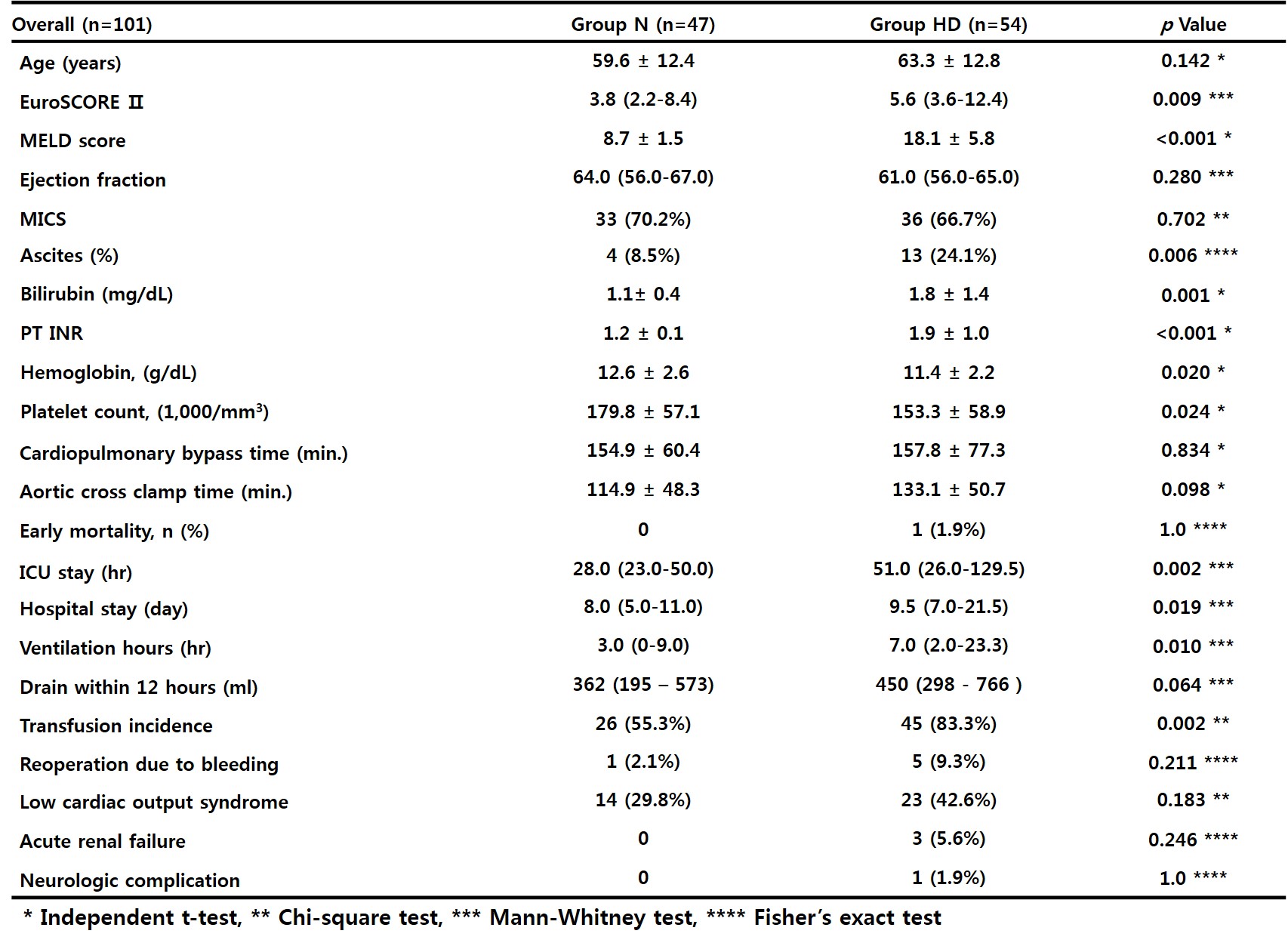
Results : Although preoperative demographics were entirely different, early postoperative course was comparable.(Table) The early death rate was 0% in the N group and 1.9% in the HD group due to pulmonary complication. No significant difference in major complications were observed. But indicators of recovery such as ICU stay, hospital stay and prolonged ventilation were significantly worse in HD group. The simplified MELD score in the HD group decreased significantly 6 months after surgery.(p<0.001)
Conclusion : Early referral of severe or moderate TR patients before they develop hepatic dysfunction could result in faster recovery. Because MELD scores improved significantly after TR surgery, the increased risk associated with HD may have little influence to conduct TR surgery even for the patients with HD.
Methods : Among 159 consecutive patients who underwent tricuspid valve surgery from October 2008 to July 2017,101 patients with moderate or severe TR were included. We divided the patients into with the normal liver function(N;n=47) and HD(n=54) groups. The definition of HD was clinically or radiologically diagnosed liver cirrhosis(n=15) or preoperative model for end-stage liver disease(MELD) score ≥13 (n=50). Perioperative variables were compared and changes in simplified MELD score following surgery were determined.
Results : Although preoperative demographics were entirely different, early postoperative course was comparable.(Table) The early death rate was 0% in the N group and 1.9% in the HD group due to pulmonary complication. No significant difference in major complications were observed. But indicators of recovery such as ICU stay, hospital stay and prolonged ventilation were significantly worse in HD group. The simplified MELD score in the HD group decreased significantly 6 months after surgery.(p<0.001)
Conclusion : Early referral of severe or moderate TR patients before they develop hepatic dysfunction could result in faster recovery. Because MELD scores improved significantly after TR surgery, the increased risk associated with HD may have little influence to conduct TR surgery even for the patients with HD.
책임저자: Hyung Gon Je
Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea
발표자: Hyung Gon Je, E-mail : jehg7332@gmail.com








