초록접수 현황
| 17F-208 | 구연 발표 |
Clinical Values of Minimally Invasive Mitral Valve Surgery in the Elderly Population
Hyung Gon Je, Mi Hee Lim, Sang-Kwon Lee, Ji Hye Lee, Hye Rim Oh
Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea
Purpose : Due to demographic changes an increasing number of elderly patients present with mitral valve disease. Minimally-invasive mitral valve surgery (MIMVS) has evolved to become the standard therapy at some centers. The aim of this study was to compare the MIMVS to the conventional full median sternotomy in the elderly population.
Methods : This retrospective analysis included 488 consecutive patients receiving a mitral valve surgery between November 2008 and July 2017. Among them, 234 patients were at the age of 60 or older. After exclusion of emergency and concomitant surgery, 29 patients underwent conventional sternotomy (Group I) while MIMVS was performed in 143 patients (Group II).
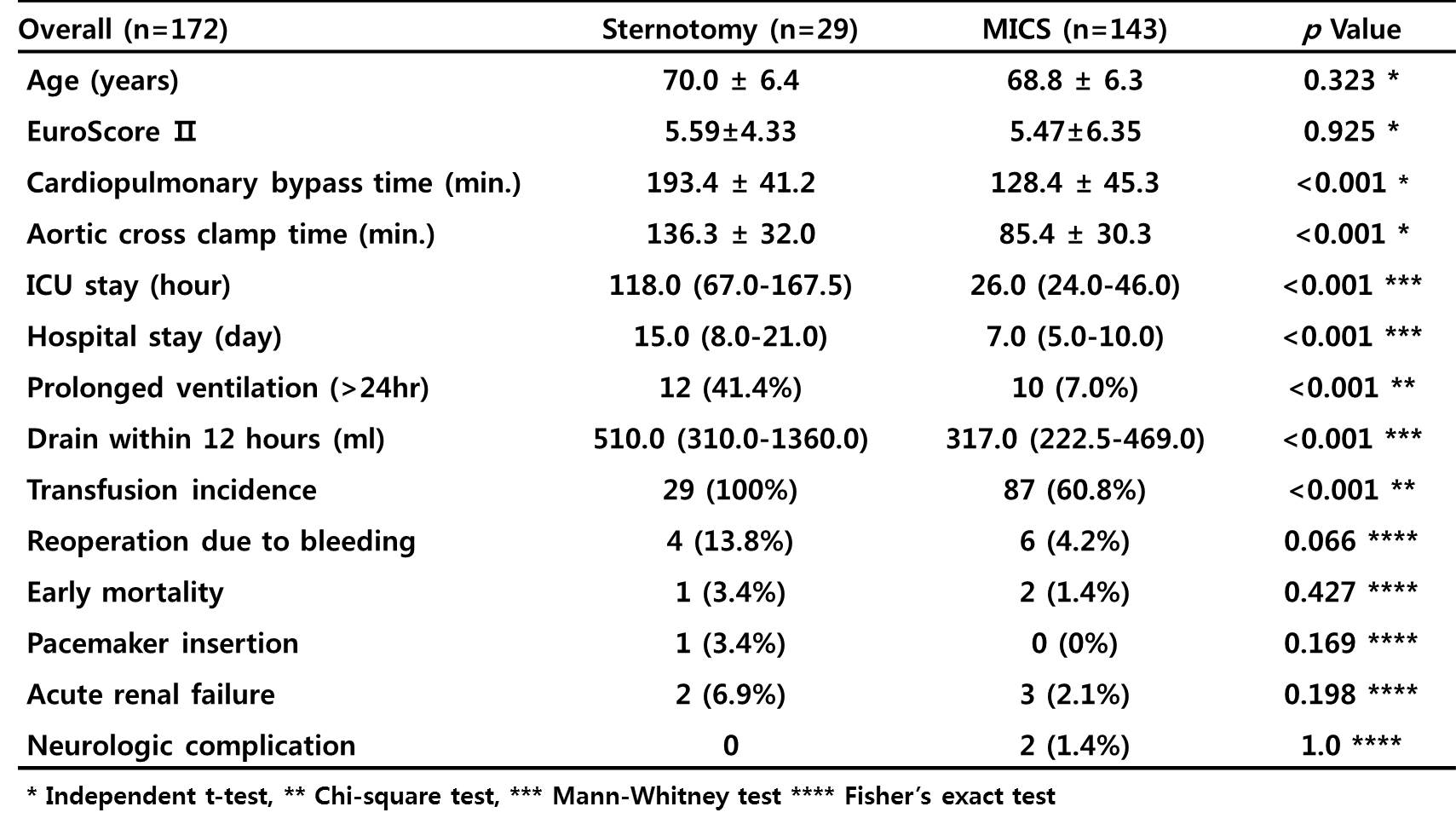
Results : Age, EuroSCORE II and left ventricular ejection fraction (I: 62.3±9.8 vs. II: 62.1±9.7; p=0.925) were similar between the two groups. Further preoperative characteristics were comparable. But aortic clamping time and were significantly longer in group I. In-hospital mortality was 3.4% group I in comparison to 1.4% in group II (p=0.427). Postoperative stroke and acute renal failure requiring dialysis were not significant different between groups. But other postoperative complications such as incidence of prolonged ventilation, and transfusion were significantly lower in group II. Following this, duration of intensive care unit and length of hospital stay were significantly shorter in group II. (Table 1.)
Conclusion : Minimally invasive mitral valve surgery is safe and feasible in elderly patients above 60 with significantly shorter ICU and in-hospital stay. Given the appropriate institutional expertise in MIMVS, such procedures can be safely performed in patients older than 60 without increasing surgical risk.
Methods : This retrospective analysis included 488 consecutive patients receiving a mitral valve surgery between November 2008 and July 2017. Among them, 234 patients were at the age of 60 or older. After exclusion of emergency and concomitant surgery, 29 patients underwent conventional sternotomy (Group I) while MIMVS was performed in 143 patients (Group II).
Results : Age, EuroSCORE II and left ventricular ejection fraction (I: 62.3±9.8 vs. II: 62.1±9.7; p=0.925) were similar between the two groups. Further preoperative characteristics were comparable. But aortic clamping time and were significantly longer in group I. In-hospital mortality was 3.4% group I in comparison to 1.4% in group II (p=0.427). Postoperative stroke and acute renal failure requiring dialysis were not significant different between groups. But other postoperative complications such as incidence of prolonged ventilation, and transfusion were significantly lower in group II. Following this, duration of intensive care unit and length of hospital stay were significantly shorter in group II. (Table 1.)
Conclusion : Minimally invasive mitral valve surgery is safe and feasible in elderly patients above 60 with significantly shorter ICU and in-hospital stay. Given the appropriate institutional expertise in MIMVS, such procedures can be safely performed in patients older than 60 without increasing surgical risk.
책임저자: Hyung Gon Je
Department of Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University College of Medicine, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea
발표자: Hyung Gon Je, E-mail : jehg7332@gmail.com








