초록접수 현황
| 17F-022 | 구연 발표 |
Establishment of a Rejection Model for Lung Transplantation using a Rat
Woo Sik Yu¹, Jin-Mo Kim², Yoon Jin Cha³, Jee Won Suh⁴, Kyoung Shik Narm⁴, Hyo Chae Paik⁴, Jin Gu Lee⁴
¹Department of Thoracic Surgery, Armed Forces Capital Hospital, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea., ²Department of Radiation Oncology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea., ³Department of Pathology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea., ⁴Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
Purpose : To investigate the pathophysiology of acute and chronic rejection and try new treatment modalities, the animal model for lung transplantation is crucial. Model using small rodent, such as a rat, has an advantage in terms of availability of inbred strain and economy. The objective of this study is to establish rejection model for lung transplantation using a rat.
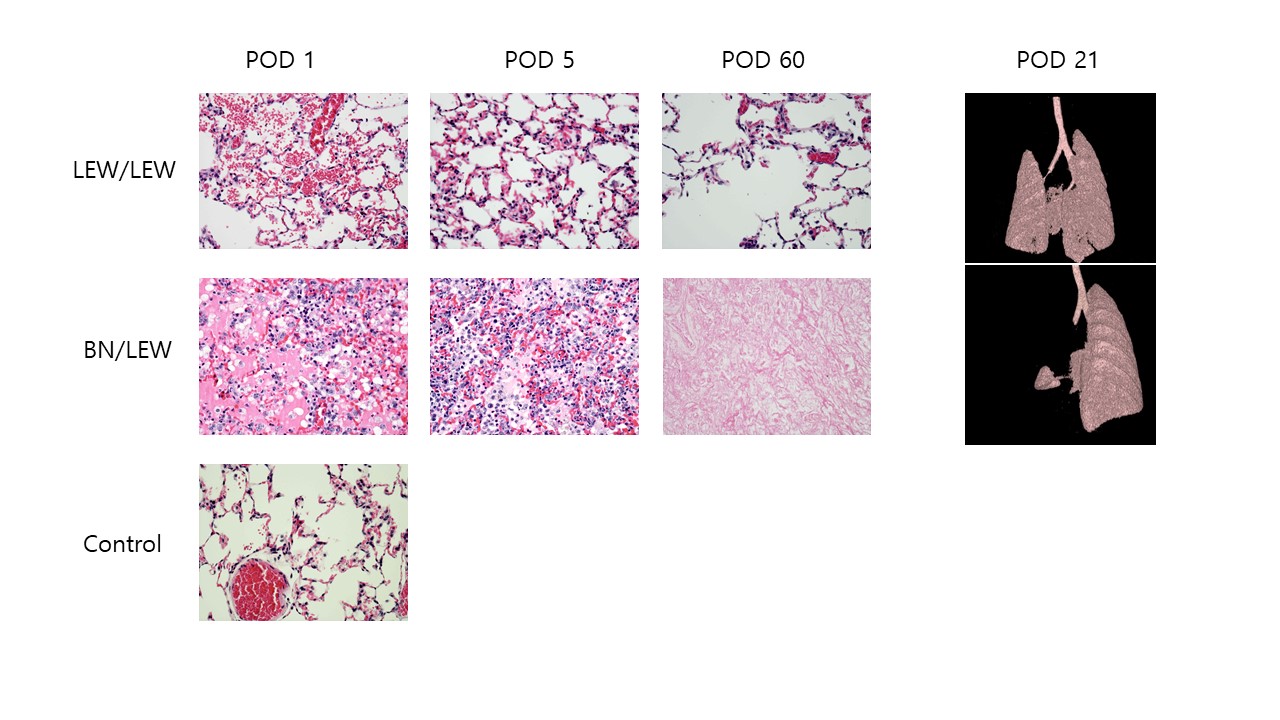
Methods : The orthotopic left lung transplantation from LEW to LEW rats (LEW/LEW) and from BN to LEW rats (BN/LEW) were performed using cuff technique. The recipient received no immunosuppression except 1mg of methylprednisolone during operation. The grafts were harvested on postoperative days (POD) 1, 3, 5, 14, and 60. CT images were obtained on POD 21
Results : The success rate of lung transplant was 83%, and there was no accidental death during the observation period. Mean ischemic time, donor preparation time, and recipient operation time were 80 ± 9, 34 ± 7 and 62 ± 6 minutes respectively. In histologic examination, LEW/LEW showed intra-alveolar hemorrhage and congestion on POD 1. it gradually recovered. On other hand, BN/LEW showed severe inflammation and necrosis earlier after transplantation, and the graft was completely replaced fibrous tissue on POD #60.
Conclusion : Lung transplantation model using rat is technically feasible, and long-term survival after lung transplantation can be achieved. This model can be used to investigate biology and treatment of acute and chronic rejection after lung transplantation.
Methods : The orthotopic left lung transplantation from LEW to LEW rats (LEW/LEW) and from BN to LEW rats (BN/LEW) were performed using cuff technique. The recipient received no immunosuppression except 1mg of methylprednisolone during operation. The grafts were harvested on postoperative days (POD) 1, 3, 5, 14, and 60. CT images were obtained on POD 21
Results : The success rate of lung transplant was 83%, and there was no accidental death during the observation period. Mean ischemic time, donor preparation time, and recipient operation time were 80 ± 9, 34 ± 7 and 62 ± 6 minutes respectively. In histologic examination, LEW/LEW showed intra-alveolar hemorrhage and congestion on POD 1. it gradually recovered. On other hand, BN/LEW showed severe inflammation and necrosis earlier after transplantation, and the graft was completely replaced fibrous tissue on POD #60.
Conclusion : Lung transplantation model using rat is technically feasible, and long-term survival after lung transplantation can be achieved. This model can be used to investigate biology and treatment of acute and chronic rejection after lung transplantation.
책임저자: Jin Gu Lee
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
발표자: Woo Sik Yu, E-mail : yws081011@gmail.com








