초록접수 현황
| 17F-099 | 구연 발표 |
Miniatured X-ray Fluoroscopic Device for Minimally Invasive Surgery
Kook Nam Han¹, Byun Hyun Choi², Hyun Koo Kim¹, Young Ho Choi¹, Jae Sung Lee², Haewook Park²
¹Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea., ²Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
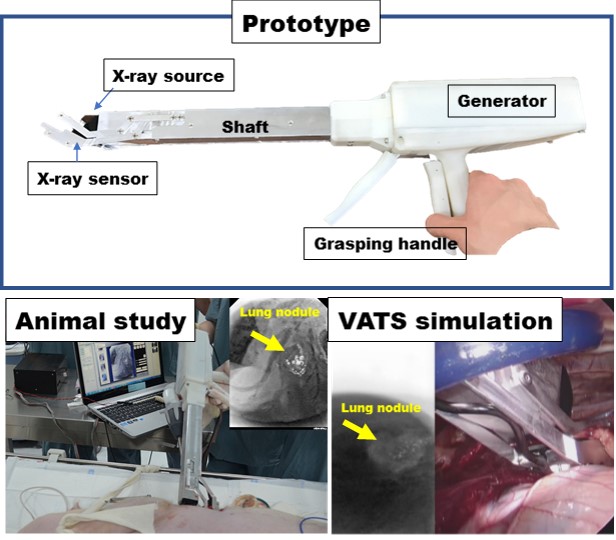
Purpose : Intraoperative detection of lung nodules marked with metallic or radiocontrast liquid marker need C-arm fluoroscopy emitting high dose radiation during VATS surgery. We developed the prototype radiographic instrument for detection of pulmonary nodules during thoracic surgery emitting low dose radiation compared with those of C-arm fluoroscopy.
Methods : We designed and fabricated the prototype miniatured X-ray radiography with similar features of endoscopic device which has long shaft body, grasping function, and potentially available for thoracoscopic surgery. Miniatured radiation tube and sensor plate were used in the development of prototype. We evaluated the prototype in animal study for potential clinical usage.
Results : The diameter of the device’s head was 4-cm length and has the grasping function at development. We tested the device for radiologic images of lung nodule at in-vivo and ex-vivo setting for clinical use. In animal models with lung nodules, we could acquire the radiologic images successfully with the device for marked lung nodules model, which were made with agar and then localized with radiocontrast. Our device showed the benefit of reduced radiation exposure less than 1/50-1/200 compared with those of C-arm fluoroscopy during mimicking VATS procedure. In preclinical studies with VATS surgery model (5-cm incision) with large animals, the devices showed the clinical potency for real time identification of lung nodules for minimal invasive surgery.
Conclusion : The prototype we developed showed extremely low radiation exposure for intraoperative radiographic localizer. Potentially, this could be furthe innovated by reducing the size of head for current VATS.
Methods : We designed and fabricated the prototype miniatured X-ray radiography with similar features of endoscopic device which has long shaft body, grasping function, and potentially available for thoracoscopic surgery. Miniatured radiation tube and sensor plate were used in the development of prototype. We evaluated the prototype in animal study for potential clinical usage.
Results : The diameter of the device’s head was 4-cm length and has the grasping function at development. We tested the device for radiologic images of lung nodule at in-vivo and ex-vivo setting for clinical use. In animal models with lung nodules, we could acquire the radiologic images successfully with the device for marked lung nodules model, which were made with agar and then localized with radiocontrast. Our device showed the benefit of reduced radiation exposure less than 1/50-1/200 compared with those of C-arm fluoroscopy during mimicking VATS procedure. In preclinical studies with VATS surgery model (5-cm incision) with large animals, the devices showed the clinical potency for real time identification of lung nodules for minimal invasive surgery.
Conclusion : The prototype we developed showed extremely low radiation exposure for intraoperative radiographic localizer. Potentially, this could be furthe innovated by reducing the size of head for current VATS.
책임저자: Hyun Koo Kim
Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
발표자: Kook Nam Han, E-mail : hdoc@korea.ac.kr








